Psoriasis
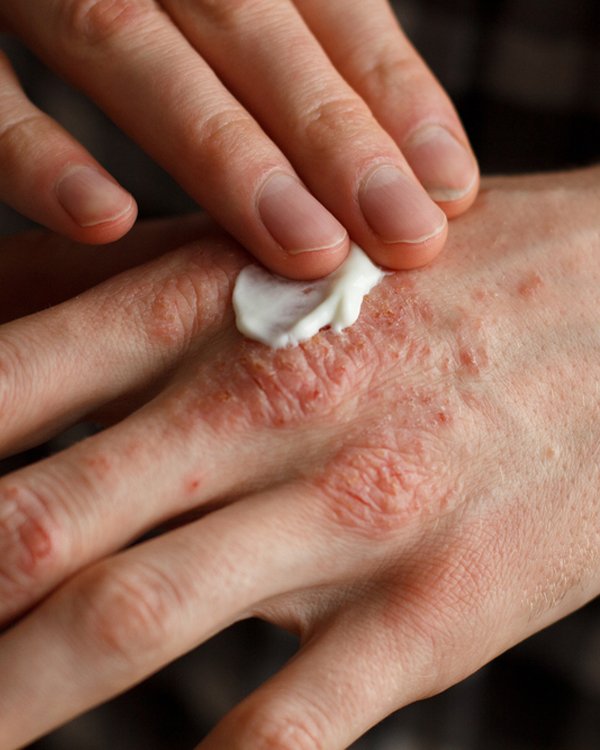
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 folds faster than average. Such a fluctuation makes the skin turn bumpy red with plaques of thick and scaly skin. Psoriasis can show skin disorder almost everywhere, but it appears mainly in the scalp, knee, elbows, and lower back.
Being an autoimmune (immunity against healthy organs) disease, the inflammation caused in the body in the form of rough skin patches is non-transferable in nature. However, some rare cases of genetic psoriasis can be observed as the autoimmune condition continues in the family hierarchy.
It is usually seen in adulthood and is expected to last not more than a couple of years. If severe, it may last for the rest of the life and would redevelop in other parts of the body and might spread to a larger scale. Although skin tissues of hands, feet, neck, and scalp are most prone to this disorder, however, some less common cases show psoriasis effect in nails, mouth, and the area around reproductive glands.
As per a study conducted in North America, approximately 7.4 million Americans have been affected with psoriasis and were commonly caused due by the following factors:
- Diabetic disorder
- Inflammatory condition
- Cardiovascular health
- Anxiety
- Depression
Although the study was conducted in the west, several known health officials in India agree to the fact that similar patterns of psoriasis causes are observed here as well. Psoriasis is complex and dynamic for its growth patterns and diagnostic difficulties.
Types of Psoriasis
Plaque Psoriasis
- It is the most common type of psoriasis found. The usual inflammatory marks of bumpy redness on the scalp, knee, hand, and elbow are observed in this type. As several studies concluded, almost 80% of the population who suffered psoriasis has been covered with this type. It is an adulthood autoimmune condition with whitish-silver plaques on the skin.
Guttate Psoriasis
- This type of psoriasis is commonly seen in childhood and shows small skin spots on the torso, arms, and legs. Although thick plaques on the skin aren’t observed as seen in plaque psoriasis, however, minimal spots can be viewed in different parts of the body at the same time.
Pustular Psoriasis
- Such a type is commonly seen in adults and shows white, pus-filled blisters and broad areas of red, inflamed skin. Small body parts like ha
- nds and feet are most prone to this disease, but widespread skin disorders can also be viewed sometimes.
Inverse Psoriasis
- The differentiating factor about this type is the bright red, skinny, and inflamed skin. The patches of inverse psoriasis are observed under armpits and breasts and have the potential to spread elsewhere as well.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
- This is the most unique and severe type of psoriasis as the skin almost looks burned and has the capacity for widespread inflammation. The patients dealing with this type are commonly affected by fever and other infectious viral.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Psoriasis differs from individual to individual on the basis of its type and the area covered, ranging from a few flakes to the whole body being affected.
- Following are some common symptoms observed:
- Red, thick and inflamed skin
- Whitish-silver plaques of scales on the skin
- Dryness in the skin and swollen throat
- Burned like skin patches
- Small flakes of pink spots
- Thick and pitted nails
- Swollen joints
- It isn’t mandatory that everyone will observe the above-stated symptoms. Psoriasis can be dynamic and uniquely severe for severe individuals, but the presence of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions seem to be common in all cases.
What causes Psoriasis:
- A few decades ago, doctors and medical experts were unsure of the reasons that cause psoriasis. But thanks to recent development in this regard, we have two fundamental causes:
Immune System
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that triggers inflammatory skin disorders in different parts of our body. An autoimmune condition is a case where our body’s immunity counters healthy organs and makes the white blood cells mistakenly attack skin cells.
- Generally, the white blood cells are responsible for attacking and destroying attacking bacteria and covering the depleted cells in that area. When the same mechanism works for an inflamed area, the skin cells multiply and form scales of thick skin.
Genetic Disorder
- As per studies concluded, the genetic inheritance with respect to psoriasis is evident to occur in just 2-3% of patients. If you are the immediate member of the elder in your family who’s suffering from psoriasis, there are high chances that you will be affected with the same.
Diagnostic Tests
- There are primarily two kinds of diagnosis available for psoriasis:
- Physical Examination
- In most cases, if the inflammatory patches appear on body parts like the scalp, knee, elbow, ear, belly button, and nails, the doctor is most likely able to determine the presence. It is so as the area affected and the scaly plaques developed on the skin gives a clear indication of this autoimmune condition. Make sure you are comfortable to show all areas of concern as this will bring more clarity to the doctor, and following this, there will be an easement in your treatment.
Lab Tests
If, in some cases, it becomes difficult for your doctor to determine if there is a presence of psoriasis or not, having a biopsy lab test for the affected skin patch would be an apt solution. A tiny fraction of skin tissue extracted will be sent for a lab test where all possibilities of skin infections can be examined. Having been injected with a numbing medication to make this process less painful for you, this type of diagnosis will provide accurate results.
Treatment of Psoriasis
- The kind of treatment involved differs based on the size of the patch, the area infected, the patient’s age and other health concerns, and the duration of the autoimmune condition.
- Your doctor will select the treatment plan accordingly.
Following are a couple of common ways used for treating psoriasis:
- Topical Medications
- This type of treatment is usually used for less intense cases of psoriasis and helps in slowing down the growing symptoms. These include:
- Steroid Creams
- Moisturizer for dry and scratchy skin
- Cool Tar – a common treatment used to heal scalp patches
- Vitamin D rich cream and ointments
- Light Therapy
- This sort of treatment uses ultraviolet lights to shine over the infected area and helps in slowing down the rate of cell formation. Since psoriasis is evidently an autoimmune condition, this therapy helps in reducing the white blood cells attacking the affected area. PUVA (photochemotherapy) is used in medicine called psoralen with a special form of ultraviolet light.
Medicinal Supplementations
- Either you have a moderate to intense case of psoriasis or other forms of treatments that have been failing to heal or both, your doctor may advise you to take some oral or injected medication. Following are commonly advised medications:
- Retinoids – These are used to reduce the symptoms temporarily. Once you stop taking these, the inflammatory condition may rise again. Hair loss and inflammation in lips are common side effects. Women associated with pregnancy in the current stage or within the next three years are not advised to take this supplement.
- Biologic treatment – These kinds of drugs reduce your body’s overall immunity to reduce the rising autoimmune condition during psoriasis.
- Cyclosporine – Similar to the class of biological medications, this drug also helps in reducing the immunity levels of your body. Unlike biological treatment. Cyclosporine drug is more intense and may cause sickness for a few days or a week. Some kidney problems and high blood pressure are common side effects.
- Apremilast – It’s a new form of drug that acts as an enzyme inhibitor to reduce the possibility of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in the long run. It is an oral medication that controls the spread of a specific enzyme responsible for slowing the potential spread of inflammation.
Dietary Changes
- There is no evidence that adding nutritious foods to your diet will completely eradicate the effects of psoriasis, but having some healthy alterations can prevent the possible spread and reduce the symptoms. Following are some advised recommendations:
- Eating less caloric food as compared to your BMR
- Fiber-rich foods
- Multivitamin tablets
- Avoid triggering foods such as red meat, refined sugar, and processed foods
- Reduction in intoxication
Conclusive Statistics
- At least 5% of the global population suffers from psoriasis once in their lifetime.
- As per WHO, approximately 75% of the people affected with psoriasis are in the age limit of 20 – 45.
- People with intense conditions of psoriasis will likely develop type 2 diabetes, kidney dysfunction, heart problems, and high blood pressure.
- The relieving fact is that in maximum cases of psoriasis, the given advanced cures are able to successfully treat various kinds of psoriasis.
- Genetic transfer of psoriasis is as rare as less than 1%
Know more about us:
- Like our Facebook Page
- Follow us on Instagram
- Subscribe to us on YouTube
[ninja_form id=3]


